Content
- What Is an Amortizable Bond Premium?
- Depreciation Rules to Recognize the Payment Pair at Maturity
- Bonds Issued At Par
- Bond Discount
- How Does Amortization of Bond Discount Work?
- The amortization of premium on bonds payable will _____________ the net income. a. increase b. decrease c. not affect d. offset
- Amortization is Necessary for Tax Purposes

If the amounts of interest expense are similar under the two methods, the straight‐line method may be used. One source of financing available to corporations is long‐term bonds. Bonds represent an obligation to repay a principal amount at a future date and pay interest, usually on a semi‐annual basis. Unlike notes payable, which normally represent an amount owed to one lender, a large number of bonds are normally issued at the same time to different lenders. These lenders, also known as investors, may sell their bonds to another investor prior to their maturity. For the remaining eight periods (there are 10 accrual or payment periods for a semi-annual bond with a maturity of five years), use the same structure presented above to calculate the amortizable bond premium. Premium BondsA premium bond refers to a financial instrument that trades in the secondary market at a price exceeding its face value.

One simple way to understand bonds issued at a premium is to view the accounting relative to counting money! If Schultz issues 100 of the 8%, 5-year bonds when the market rate of interest is only 6%, then the cash received is https://simple-accounting.org/ $108,530 . Schultz will have to repay a total of $140,000 ($4,000 every 6 months for 5 years, plus $100,000 at maturity). In order to calculate the premium amortization, you must determine the yield to maturity of a bond.
What Is an Amortizable Bond Premium?
He has over 40 years of experience in business and finance, including as a Vice President for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Texas. He has a BBA in Industrial Management from the University of Texas at Austin. Par value can refer to either the face value of a bond or the stock value stated in the corporate charter.
Is premium on bonds payable a debit or credit?
If there was a premium on bonds payable, then the entry is a debit to premium on bonds payable and a credit to interest expense; this has the effect of reducing the overall interest expense recorded by the issuer.
The premium on bonds payable account is shown on the balance sheet as A contra asset. Credit the bond premium account the value of the bond premium. In this case, you’ll credit bond premium account for $4,100.Note that the complete accounting from this step and the previous one keeps your books in balance. You’ve debited cash for $104,100 and you’ve credited two accounts for $104,100 ($100,000 + $4,100).
Depreciation Rules to Recognize the Payment Pair at Maturity
Based on market conditions, the price could be less than or greater than $1,000. An investor will agree to lend their money because a bond specifies compensation in the form of interest. The interest terms on a bond will vary, but essentially the lender will demand interest to compensate for the opportunity cost of providing the funding and the credit risk of the borrower. See a comparison between secured vs unsecured bonds, and term bonds vs serial bonds. The Treasury yield is the interest rate that the U.S. government pays to borrow money for different lengths of time. Accretion of discount is the increase in the value of a discounted instrument as time passes and the maturity date looms closer.
Good Faith Deposit – An amount not less than 1% of the par amount of the bonds that an underwriter electronically transfers to IU approximately 7 to 14 days prior to the closing on the sale of the bonds. Total interest expense is equal to amounts paid by the issuer to the creditor in excess of the amount received. Initial liability is the amount paid to the issuer by the lender. The amount may not equal to the face value of the bond.
Bonds Issued At Par
See Table 4 for interest expense and carrying value calculations over the life of the bonds using the effective interest method of amortizing the premium. At maturity, the General Journal entry to record the principal repayment is shown in the entry that follows Table 4 .
Amortizable Bond Premium Definition – Investopedia
Amortizable Bond Premium Definition.
Posted: Sun, 26 Mar 2017 00:34:28 GMT [source]
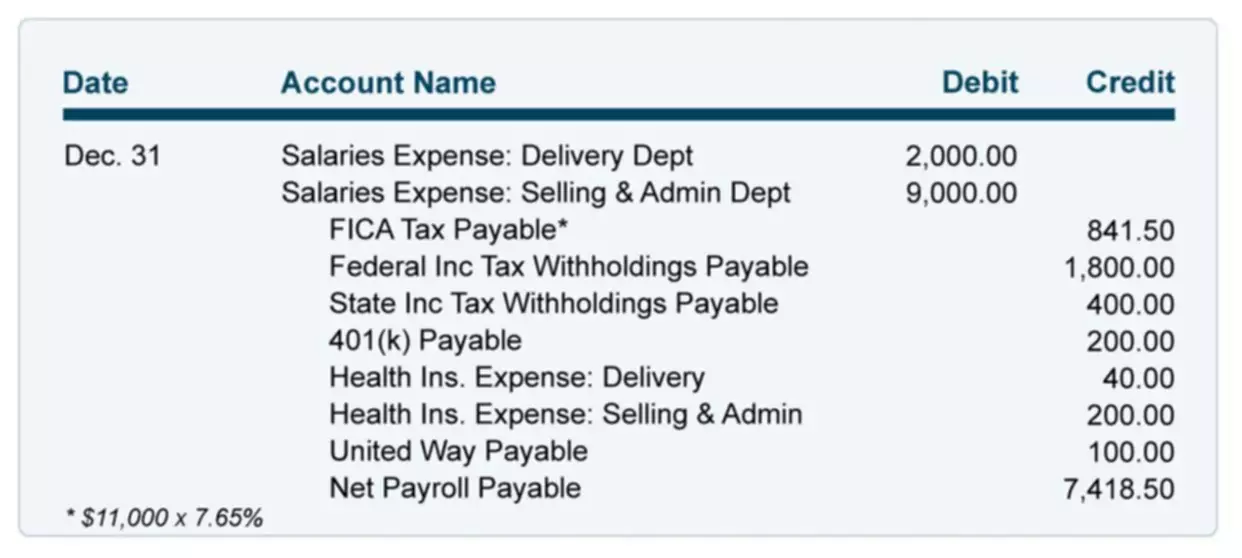
AmortizationAmortization of Intangible Assets refers to the method by which the cost of the company’s various intangible assets is expensed over a specific time period. This time frame is typically the expected life of the asset. The corporation must make an interest payment of $4,500 ($100,000 x 9% x 6/12) on each June 30 and December 31.
Bond Discount
Regardless of when the bonds are physically issued, interest starts to accrue from the most recent interest date. Firms report bonds to be selling at a stated price “plus accrued interest.” The issuer must pay holders of the bonds a full six months’ interest at each interest date. amortization of premium on bonds payable Thus, investors purchasing bonds after the bonds begin to accrue interest must pay the seller for the unearned interest accrued since the preceding interest date. The bondholders are reimbursed for this accrued interest when they receive their first six months’ interest check.
Unlike discount bonds , they make no coupon payments so they have no effect on reported CFO. In essence, zero-coupon bonds are a special type of discount bonds. Therefore, their effects on financial statements are similar to those of discount bonds. Those resulting from financing activities include short-term debt and the current portion of long-term debt.
In the same transaction, you debit interest expense for $40,900 and credit interest payable or cash for $45,000. A common factor between bond amortization and indirect cash flow method is that both of them involve interest expenses which are not in cash. In the indirect cash flow method, the expenses not in cash are adjusted to the net income . With the amortization of bonds, a discount or adjustment is promoted. The change to the net income is either an addition or subtraction depending on the bond redemption type. The amortization of bonds is a process where the premium or discounted amount is assigned to the payment of interest of each period of the validity of the bond.